


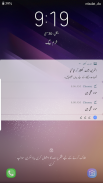

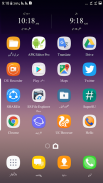
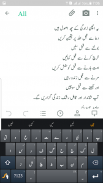


Jameel Noori Nastaleeq FlipFont

คำอธิบายของJameel Noori Nastaleeq FlipFont
Nastaʿlīq (Persian: نستعلیق, from نسخ Naskh and تعلیق Taʿlīq) is one of the main calligraphic hands used in writing the Persian script, and traditionally the predominant style in Persian calligraphy.[1] It was developed in Iran in the 14th and 15th centuries.[2] It is sometimes used to write Arabic-language text (where it is known as Taʿliq[citation needed] or Persian and is mainly used for titles and headings), but its use has always been more popular in the Persian, Turkic and Urdu sphere of influence. Nastaʿlīq has extensively been (and still is) practised in Iran, Pakistan, India, Afghanistan and other countries for written poetry and as a form of art.
A less elaborate version of Nastaʿlīq serves as the preferred style for writing in Kashmiri, Punjabi and Urdu, and it is often used alongside Naskh for Pashto. In Persian it is used for poetry only. Nastaʿlīq was historically used for writing Ottoman Turkish, where it was known as tâlik[3] (not to be confused with a totally different Persian style, also called taʿlīq; to distinguish the two, Ottomans referred to the latter as taʿlīq-i qadim, "old taʿlīq").
Nastaʿlīq is the core script of the post-Sassanid Persian writing tradition, and is equally important in the areas under its cultural influence. The languages of Iran (Western Persian, Azeri, Balochi, Kurdi, Luri, etc.), Afghanistan (Dari, Pashto, Uzbek, Turkmen, etc.), Pakistan (Punjabi, Urdu, Kashmiri, Saraiki, etc.), and the Turkic Uyghur language of the Chinese province of Xinjiang, rely on Nastaʿlīq. Under the name taʿliq (lit. “suspending [script]”), it was also beloved by Ottoman calligraphers who developed the Diwani (divanî) and Ruqah (rık’a) styles from it.
Nastaʿlīq is amongst the most fluid calligraphy styles for the Arabic alphabet. It has short verticals with no serifs, and long horizontal strokes. It is written using a piece of trimmed reed with a tip of 5–10 mm (0.2–0.4 in), called qalam ("pen", in Arabic and Persian قلم), and carbon ink, named davat. The nib of a qalam can be split in the middle to facilitate ink absorption.
Two important forms of Nastaʿlīq panels are Chalipa and Siah-Mashq. A Chalipa ("cross", in Persian) panel usually consists of four diagonal hemistiches (half-lines) of poetry, clearly signifying a moral, ethical or poetic concept. Siah-Mashq ("black drill") panels, however, communicate via composition and form, rather than content. In Siah-Mashq, repeating a few letters or words (sometimes even one) virtually inks the whole panel. The content is thus of less significance and not clearly accessible.
For more detail:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nasta%CA%BFl%C4%ABq_script
Nasta'līq (เปอร์เซีย: نستعلیقจากنسخ Naskh และتعلیقTa'līq). เป็นหนึ่งในมือช้อยหลักที่ใช้ในการเขียนสคริปต์เปอร์เซียและแบบดั้งเดิมสไตล์ที่โดดเด่นในการประดิษฐ์ตัวอักษรภาษาเปอร์เซีย [1] ได้รับการพัฒนาในอิหร่านในศตวรรษที่ 14 และ 15. [2] มันเป็นบางครั้งใช้ในการเขียนข้อความภาษาอาหรับภาษา (ที่เป็นที่รู้จักกัน Ta'liq [อ้างจำเป็น] หรือเปอร์เซียและส่วนใหญ่จะใช้สำหรับชื่อและส่วนหัว) แต่ใช้งานได้เสมอที่นิยมมากขึ้นในเปอร์เซียเตอร์กและภาษาอูรดูรูปทรงกลมของ มีอิทธิพล Nasta'līqได้รับอย่างกว้างขวาง (และยังเป็น) ได้รับการฝึกฝนในอิหร่าน, ปากีสถาน, อินเดีย, อัฟกานิสถานและประเทศอื่น ๆ เพื่อเขียนบทกวีและเป็นรูปแบบของศิลปะ
รุ่นที่ซับซ้อนน้อยกว่าของNasta'līqทำหน้าที่เป็นรูปแบบที่ต้องการสำหรับการเขียนในแคชเมียร์, ปัญจาบและภาษาอูรดูและมันมักจะถูกนำมาใช้ควบคู่ไปกับ Naskh สำหรับ Pashto ในเปอร์เซียจะใช้สำหรับบทกวีเท่านั้น Nasta'līqถูกนำมาใช้ในอดีตสำหรับการเขียนตุรกีที่มันเป็นที่รู้จักกันtâlik [3] (เพื่อไม่ให้สับสนกับสไตล์เปอร์เซียที่แตกต่างกันโดยสิ้นเชิงเรียกว่าta'līq; แยกแยะความแตกต่างทั้งสองออตโตมาจะเรียกว่าหลังเป็นta'līqฉัน Qadim, "ta'līqเก่า")
Nasta'līqเป็นสคริปต์หลักของการโพสต์ยะห์เขียนประเพณีเปอร์เซียและมีความสำคัญเท่าเทียมกันในพื้นที่ภายใต้อิทธิพลทางวัฒนธรรมของตน ภาษาของประเทศอิหร่าน (ตะวันตกเปอร์เซียเซอร์รีบา Kurdi, Luri ฯลฯ ) อัฟกานิสถาน (Dari, Pashto, อุซเบกิ, เติร์กเมนิสถาน, ฯลฯ ) ปากีสถาน (ปัญจาบภาษาอูรดูแคชเมียร์ Saraiki ฯลฯ ) และ ภาษาเตอร์กอุยกูร์ของจีนจังหวัดของซินเจียงพึ่งพาNasta'līq ภายใต้ชื่อ ta'liq (จุดนี้“ระงับ [สคริปต์]”) มันก็เป็นที่รักของออตโตมันช่างประดิษฐ์อักษรที่พัฒนา Diwani (Divani) และ Ruqah (rık'a) รูปแบบจากมัน
Nasta'līqเป็นหนึ่งในรูปแบบการประดิษฐ์ตัวอักษรของเหลวมากที่สุดสำหรับตัวอักษรภาษาอาหรับ แต่ก็มีแนวดิ่งสั้นไม่มีเซอริฟและจังหวะแนวนอนยาว มันถูกเขียนโดยใช้ชิ้นส่วนของการตัดแต่งกกด้วยปลาย 5-10 มิลลิเมตร (0.2-0.4 ใน) ที่เรียกว่า qalam ( "ปากกา" ในภาษาอาหรับและเปอร์เซียقلم) และหมึกคาร์บอนชื่อ Davat ปลายปากกาของ qalam สามารถแยกที่อยู่ตรงกลางเพื่อความสะดวกในการดูดซึมหมึก
สองรูปแบบที่สำคัญของแผงNasta'līqเป็น Chalipa และ Siah-Mashq Chalipa ( "ข้าม" ในเปอร์เซีย) แผงมักจะประกอบด้วยสี่ hemistiches แนวทแยง (ครึ่งสาย) ของบทกวีอย่างเห็นได้ชัด signifying คุณธรรมจริยธรรมหรือบทกวีแนวคิด Siah-Mashq ( "เจาะดำ") แผง แต่สื่อสารผ่านองค์ประกอบและรูปแบบมากกว่าเนื้อหา ใน Siah-Mashq ซ้ำตัวอักษรไม่กี่หรือคำ (บางครั้งแม้แต่คนเดียว) แทบหมึกทั้งแผง เนื้อหาจึงมีความสำคัญน้อยลงและไม่สามารถเข้าถึงได้อย่างชัดเจน
สำหรับรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมได้ที่: https: //en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nasta%CA%BFl%C4%ABq_script

























